How Much Does the Government Subsidize Beef
Should governments subsidise the meat and dairy industries ?

Price is a very powerful tool to manipulate our consumption decisions. The amount of money governments pay as a subsidy to keep the cost of sure bolt low is one of the about important factors affecting national and global food consumption. Meat and dairy industry equally one of leading sector of the economic system receives huge direct and indirect subsidies from governments in many countries, provoking huge business organization because of the impact it has on human health, the environment protection, and on animals right. Denmark, for instance, is currently considering a recommendation from its ideals council that all red meats should exist taxed. The quango argued in May that citizens were indeed "ethically obliged" to reduce their consumption to curb greenhouse gas emissions.
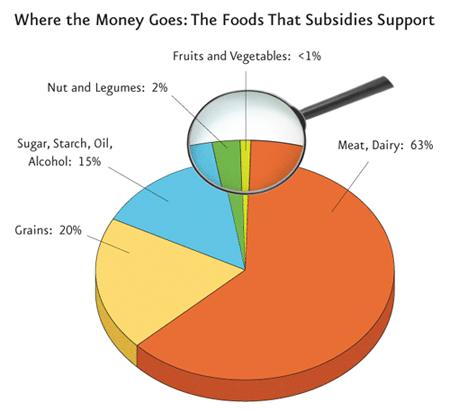
Why does it thing?
The amount of subsidy governments pay to meat and dairy industry is striking to many, if non very surprising. According to contempo information from Metonomics, the American government spends $38 billion each year to subsidize the meat and dairy industries, only only 0.04 percentage of that (i.east., $17 meg) each year to subsidize fruits and vegetables.
Subsidizing the dairy and meat production volition obviously reduce their price. When the price of something is lower, people tend to consume more than of it. This is one of the reasons why meat and other dairy products become a larger share of our daily consumption.
The same is true in the European Union, over the concluding l years, there has been an exponential increment in the consumption of animate being products. Despite this huge increase in demand these items cost extremely little. This is because of the fact that the dairy manufacture receives huge corporeality of subsidies both from the matrimony and fellow member states. The Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) of Eu provides agricultural subsidies which according to the European Commission costs each European union citizen around 30 euro cents a day. Every bit the Union'due south most expensive programme which almost represent 40% of the EU'due south budget, CAP provides €53 billion a year every bit a subsidy for agricultural products which include meat and diary products.
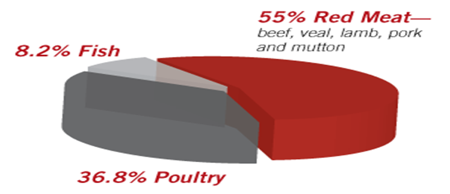
Western diets are highly characterized by a high intake of animal products. The data from System for Economic Cooperation and development (OECD) shows that in 2014 the average American adult consumed ninety kilograms (198 pounds) of meat in 2014. The global average during that same yr was 34 kilograms (75 pounds). By 2024, these numbers are projected to increase to 94.1 kilograms (207.5 pounds) per person in the U.S. and 35.5 kilograms (78.3 pounds) globally.
The size of meat and diary industry is thus immense. The North American Meat Institute estimate that, in full, the meat manufacture contributes nearly $894 billion to the US economy. Beef lone is a 95 billion a year a year business. In 2015, in all industries involved in meat production with all suppliers, distributors and retailers this industry employees around 6.2 million people with full wage of $200 billion. All these dimensions affects the full toll of meat consumption borne by the guild, like this short video well recaps:
The ethical dilemma
I may wonder why are those subsidies a trouble since the Humans won the struggle for life by eating meat for centuries. What is incorrect with helping an industry that feeds you and has evidently nothing morally reluctant? What is incorrect with giving admission to meat and to a and so-chosen balanced nutrition to as many people every bit possible? What is the ethical dilemma hither? We actually feel furthermore prompted to question this issue that no one is questioning information technology, while it is completely part of his/her daily life — say, well-hidden in his/her fridge shelves.
We do think that information technology is counter-intuitive to subsidise an industry that is already the bigger i, that has the biggest lands, the best performing machines and the all-time organized production process, whereas an increasing number of small farmers are endmost their local enterprises effectually the world.
As mentioned to a higher place, information technology is striking that nobody, at an individual level but also to a higher place, questions this situation. Such a practice appears deeply anchored and institutionalized from both a historical and a cultural betoken of view, although everyone in the earth agrees that we can't reasonably keep on eating the aforementioned corporeality of meat that nosotros were used to, since we are a growing number of people in an increasingly polluted planet.
It seems more and more difficult to deny that such an industry is not providing skillful-quality products to the final consumers. Ethical concerns would not heighten if traceability of the goods was clear, equally well as their healthiness. Likewise basically denying the threat to the consumers' health, the large-calibration production process is primarily denying animal rights and decency.
Information technology is thus obvious to us that subsidizing the meat and dairy industry is not pursuing the best possible equilibrium in terms of equity. It is highly contradictory in the sense that, on i side, this policy helps people to have a wide access to food then that they alive well, but at the aforementioned fourth dimension, it is a concrete and daily threat to their wellness, to their close surroundings, and to other living beings which they share the aforementioned physical characteristics before being humans. Following the utilitarian approach, we are promoting a policy which aims at researching the all-time outcomes to as many people every bit possible.
If there may be zippo wrong with milk, the social habit to swallow information technology daily is somewhat peremptory… Before reading the main arguments for supporting our answer, you should thus first recall twice when watching the two following milk Television receiver advertisings, and just realize that you lot are part of a social construction which encourages you to consume milk proteins at every footstep of your life — whose highest authorities can either be your Mum or your Bollywood dancing partner !
Environment and climate change
Whilst arguments concerning animal rights tin be used to justify the end of regime subsidies of the meat and dairy industries, it is possible to expect at this question from a purely human perspective. There is a fair amount of disagreement as to how much importance should exist placed on fauna suffering or beast life. Virtually of us are desensitized to this a few days after seeing a horrific butchery video. Almost governments are more concerned with their voters and their citizen's concerns. These concerns can exist quite selfish. This is why, when discussing public policy, it is important to consider citizens. Many countries are or at to the lowest degree claim to be committed to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and slowing downwards the process of climate change. Much similar for the COP21 in Paris last year, countries regularly make commitments in order to keep global warming under the two°C threshold. This effort is more often than not focussed on reducing greenhouse gas emission, well-nigh notably carbon dioxide. It is fair to agree that global warming is a business organization, does or will affect inhabitants of our planet negatively and should be prevented.
However, meat and dairy product are 1 of the biggest sources of CO2. The United nations's FAO (Food and Agriculture Organisation) estimates that livestock is responsible for 18% of global CO2 emissions[1].It also consumes more h2o and land, precious and rare natural resources that could be used for vegan food production instead. Government subsidies of this industry is not only damaging for the environment only likewise inconsistent with their claimed goals and international commitments. Information technology is unrealistic to combat climate change effectively without considering the impact of the food industry. Pollution and other negative ecology consequences are negative externalities. This means they are non taken into account by the market cost of a good. This is the case with meat. Subsidies, in the way they are carried out today are counterproductive. They assistance lower the cost of meat and dairy products. Not just is their cost not representative of the ecology toll, it is not even representative of the real production cost. This allows meat and dairy farmers to produce cheap meat profitably, despite its detrimental effects on the environs.
This is a stiff argument against government subsidies. Helping reduce meat production and consumption would be an effective style of reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This is compatible with a utilitarian ethical perspective. It would also help countries to honour their international commitments, which is deontologically more than upstanding. Stopping subsidies towards these industries and favouring others could fifty-fifty exist more efficient, produce more than food at a lower cost to government considering more environmentally friendly agriculture is more sustainable from both an ecological and an economical perspective. Furthermore, environmental reasons are already used for other forms of public action (incentivising the utilise of public send for example). This is an equally if not more than valid statement for adjusting agricultural subsidy policies in a similar fashion, in order to affect what we produce and consume.
Health issues
Providing food cannot be totally equity-oriented if not taking care almost health and sanitary issues. Of grade, getting food maximizes your utility in accented terms merely the economical theory also suggests that the marginal utility decreases with quantity. Even though a good such as nutrient is a vital demand, we can get enough of it considering of our body'southward natural satiety limit. Hence, subsidies to the dairy and meat industries cannot be a sustainable policy incentive in terms of equity if it is not role of a apparent comprehensive framework that ameliorate people'due south health and well-beingness.
The link betwixt existence in good health and consuming meat and dairy products every day is nonetheless not clearly established. On i side, the fact that it has been a repeated public policy recommendation since the end of the Second Globe War in the adult economies doesn't help to cast doubt on its effects. Just on the other side, this fact offers an adequate field for long-term studies about meat and milk high-consumption effects on cancer, heart diseases, diabetes or obesity, given that all these diseases take reached disturbing proportions in our societies during the final l years.
According to the American health researcher Joe Keon in his 2011 book 'Whitewash: The Agonizing Truth About Cow's Milk and Your Health', the largest epidemiological study ever, really from China, showed a straight relationship between dairy consumption and cancer — the more dairy, the more cancer. He also suggests that nosotros should think difficult about consuming the moo-cow's milk since no other animal species drinks the milk of some other species, and that no other species drinks milk after a very young age.
If, even so, policy makers have to go beyond correlations and get strong scientific causations in social club to support their policy decisions, the doubt is enough to seriously reconsider the framework for public action and, at least, think about reducing the global level of meat consumption. The mere precautionary principle is a sufficient ethical statement to rethink the current measures assuasive the dairy and meat industries' processes.
Animal ethics
" Animals are not ours to eat, habiliment, experiment on, utilise for entertainment or abuse in any other manner."
Peter vocaliser, a famous utilitarian and virtually influential advocator of animal correct argues that humans and animals share an important aspect of equality, in the capacity to endure or to enjoy their lives. In his interview at the Carnegie Council for Ethics in International Affairs on October 6, 2011, he says:
"I think in terms of equality between humans and animals, in a very specific sense, the sense in which they practice share an important equality, and that is the capacity to suffer or enjoy their lives. What I am opposing is discounting or ignoring the pain of animal beings, but because they are not members of our species. I desire to extend equality beyond the species purlieus. We should give equal consideration to the interests of all beings, all beings accept interests, all tin can feel pain, irrespective of their species."
Merely in a reality things are unfortunately quite dissimilar. One recent report titled the Economic science of Meat Consumption by Jon Haveman shows that ix.i billion land animals, eight.7 billion chickens and 400 meg cows, pigs, ducks, and turkeys are beingness ruthlessly killed to to feed only US consumers every single year. Of which over 99% of subcontract animals are raised in factory farms, which only focus on maximizing profit at the expense of the animals' welfare. Worldwide information from Animalequality shows that over 56 billion farmed animals are killed every yr by humans. These figures exercise not even include fish and other sea creatures.
Obvious human and social aspects
We have considered the upstanding implications of these subsidies on humans. In this case, we cannot fail the benefits of such subsidies. Firstly, it is worth considering the people who piece of work in this sector. Their livelihoods depend on the meat and dairy manufacture and they rely heavily on subsidies. If the government were to end their subsidies abruptly many of these people would lose their jobs or non be able to sustain their farming. While this is obviously to be considered in making an ethical decision information technology is worth noting that these consequences to the terminate of subsidies are also a reason for this end. If it had no touch on the size and shape of the industry, at that place would exist no real ethical argument for irresolute annihilation, at least from a consequentialist betoken of view. Nevertheless, nosotros cannot deny that this would exist unpopular with those working in this industry. They could transition to a different form of farming but this would however take time and be difficult. This is directly comparable to the negative effects of the subsidies because information technology affects human beings.
All humans and in fact all of the planet's inhabitants are affected past the ecology impact of the industry, including those that piece of work in it. We are non all afflicted as depending on where we live and also on the generation we belong to. It is likely that future generations volition be worse affected. If we consider that all humans are equal the loss to these workers' livelihoods is less important to the global effect on human life, let alone the other lifeforms on the planet. In the aforementioned mode, the negative wellness effects of the electric current meat consumption, upheld by authorities subsidies, are more morally significant considering they touch more than people in an manner that is more than or less equivalent to the chore losses.

The other consequence is more cultural. Traditional foods can be an important role of national or regional cultural identity. These dishes and foods ofttimes involve meat and dairy products. What is an English breakfast without bacon,a Christmas dinner without turkey, France without cheese? This tin be taken into consideration. Cultural identity is important. However we debate that it is not as important as homo connected survival on planet earth or our wellness. It is more complicated to compare with animal well-being. Stopping these governmental subsidies would not destroy a national or regional identity. Information technology might weaken the importance of certain foods or dishes as role of this civilization merely this seems like a small toll to pay for other benefits to reducing the weight of the meat and dairy industry on our planet.
What to do ?
This issue has many ethical implications that concern different aspects of human life, our surroundings and planet, our health, our culture and way of living also as our work and livelihoods. It also, more obviously affects, animals in the fashion they are bred and raised, the suffering they endure and how their life is concluded. Subsidies may not have synthetic the current meat and dairy industry only it supports information technology and favours mass production and the continued mass consumption of these products as a office of normal life. They proceed to support an industry which is not fifty-fifty sustainable on its ain economically, let alone from an ecological perspective. This is based on old aims of ensuring food security in terms of quantity. In the Eu or the US, this is simply no longer necessary or efficient.
These subsidies are worth questioning from an ethical standpoint and we believe that these ethical concerns should be relevant to government activeness. Whether or non you choose to factor in creature wellbeing, environmental and public health concerns are already well-established policy areas. Readjusting subsidies would change the incentives in the agricultural manufacture would nonetheless leave a sure corporeality of liberty in both production and consumption only would only favour a more ethical and sustainable system which would benefit citizens' health and their living environs.
It seems clear that changing the subsidy organization is an ethical imperative. However, we do recognise that this has political implications. The agricultural industry has meaning lobbying power and political clout. This makes elected officials hesitant to act. This does not diminish the ethical necessity of action simply it is worth because transition measures and complementary policies to ease this drastic change. Here are some policy ideas to consider:
- Back up smaller farmers
The bigger the company, the college the revenue enhancement should be (to a sure threshold). The smaller is the farm, the higher should exist the subsidy (to a sure threshold also), and then that you defend local agriculture as well as local traditions and processes, with, patently, meliorate regulations on animal protection — cows' welfare in our instance. This would assist increase the quality of the products on offer
- Subsidise the production of meat alternatives like vegetables loftier in calcium or pulses high in protein.
Environmental factors should be prioritised. Subsidies could allow farmers to produce more eco-friendly produce without increasing prices for consumers to an excessive degree.
- Reform the educational activity program in schools concerning a balanced diet to represent modern science and more diverse diets.
This does not necessarily hateful promoting vegetarianism or veganism solely merely past giving a balanced view of different diets, recognising that meat and dairy are non essential to our diets and presenting the negative consequences of our current meat and dairy consumption. This could assist reduce the meat bias in our society.
- Develop incentives and nudging on reducing meat and dairy products consumption
This may only be possible in public establishments such as school cantines.
- Modify the subsidy structure gradually over several years
This could serve to ease the transition and in the meantime, alternative training could be offered to livestock farmers in order to accompany their transition into hopefully more sustainable agriculture.
[1] The Livestock, Environment and Evolution initiative, "Livestock'due south long shadow, environmental issues and options", Food and Agronomics Arrangement of the United nations, Rome, 2006.
Friends of the Earth Europe, "Meat Atlas — facts and figures about what we eat", Heinrich Böll Foundation, Berlin, January 2014, 68 pages.
erlandsonnaal1948.blogspot.com
Source: https://medium.com/@laletur/should-governments-subsidy-the-meat-and-dairy-industries-6ce59e68d26#:~:text=According%20to%20recent%20data%20from,will%20obviously%20reduce%20their%20price.
0 Response to "How Much Does the Government Subsidize Beef"
Post a Comment